An endoscopy can help healthcare professionals diagnose stomach cancer. The test uses a camera to see the stomach and help with taking a biopsy of the tissue.
An endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure. It involves inserting an endoscope, a thin instrument with a camera on the end of it, into the mouth and down to the stomach.
A doctor may order an endoscopy alongside other tests if they suspect stomach cancer.
Keep reading for more information on when doctors may recommend the procedure, as well as what to expect, general accuracy, and more.
View the slideshow below for endoscopy photos of stomach cancer.
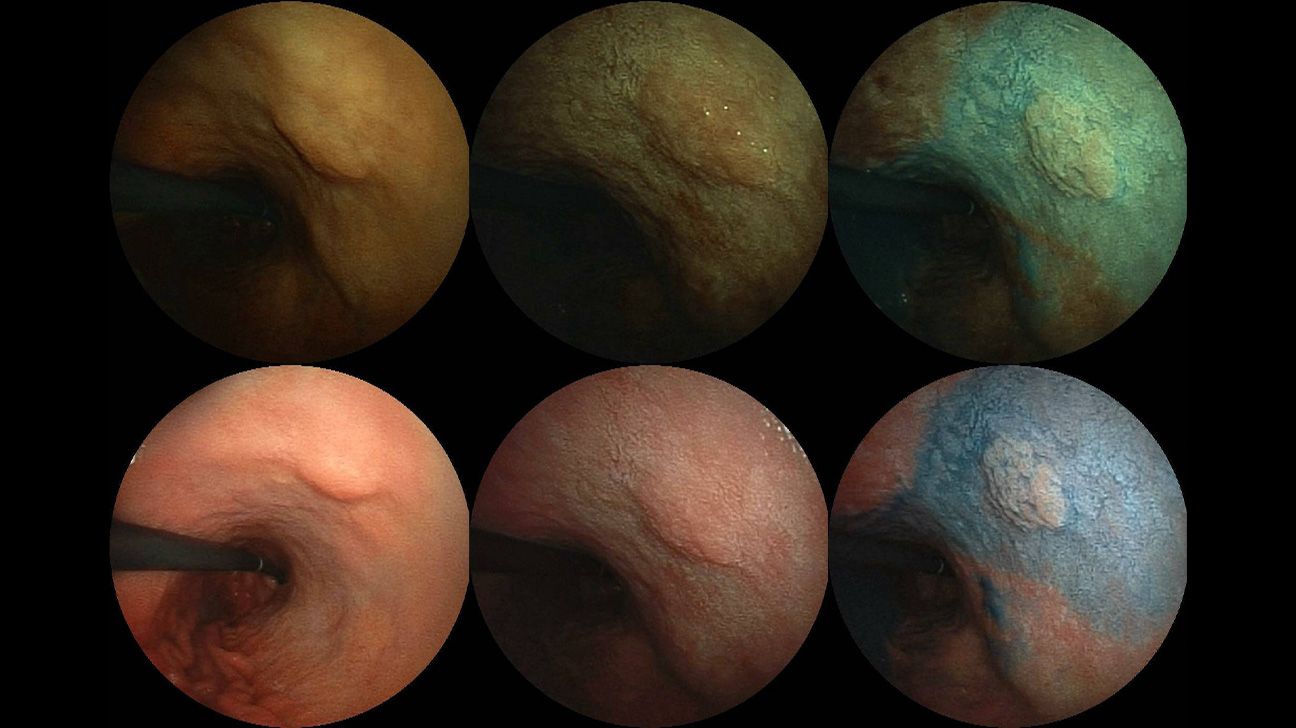
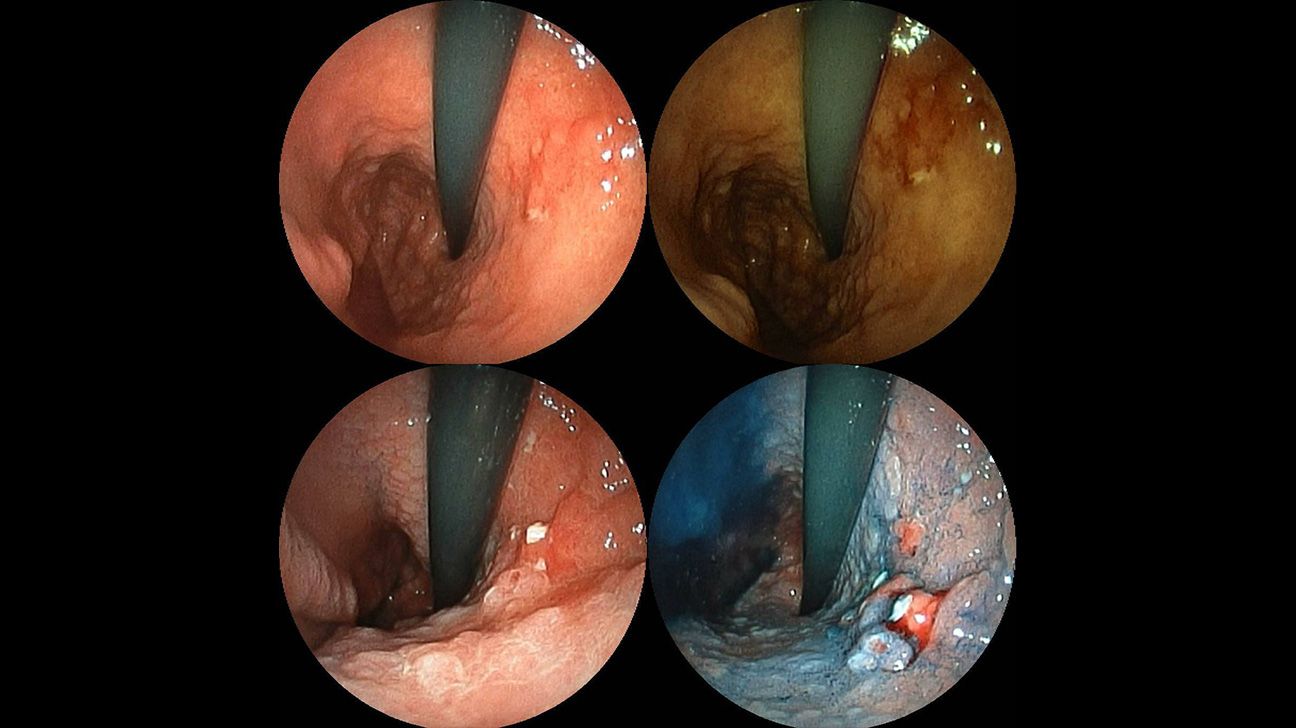
An endoscopy
However, the cancer can be harder to detect and biopsy if the cancer begins deep in the stomach wall. In these cases, a person may require endoscopic ultrasound.
Learn about endoscopy for stomach ulcers.
Endoscopies can provide a diagnostic tool for stomach cancer. An endoscopy allows a doctor to take a sample of tissue from the stomach, esophagus, or upper portion of the intestine, known as the duodenum.
A healthcare professional
- having a personal or family history of stomach cancer
- being an older individual with chronic gastric atrophy or pernicious anemia
- having certain genetic syndromes or conditions,
such asTrusted Source familial adenomatous polyposis or familial intestinal gastric cancer (FIGC) - undergoing a partial gastrectomy
- living in countries where the condition is more common, including those in Eastern Europe, South and Central America, and East Asia
Additionally, healthcare professionals
- persistent abdominal pain
- unexplained weight loss
- nausea
- dysphagia, or trouble swallowing
- getting full quickly
- hematemesis, where internal bleeding results in vomiting blood
- indigestion
Learn more about symptoms of stomach cancer.
An upper endoscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic test.
It involves a doctor inserting a flexible tube known as an endoscope into the mouth. The endoscope is equipped with a camera and other tools, allowing the healthcare professional to see inside the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
When inside, they can use the tools to take a small sample of tissue from areas that they suspect may be cancerous. They can then remove the tissue and send it to a lab for analysis.
A person may need to not eat for at least
During endoscopy, a person is usually sedated to avoid discomfort. They will generally be able to go home after a short recovery time as the anesthesia wears off.
A person will likely need to make plans for how they will get home following the procedure and plan to have someone drive them if needed.
In a
A
However, they also note that the skill and experience of the person performing the endoscopy procedure can make a difference in early detection.
Diagnostic tools often used in addition to an endoscopy with biopsy
- barium swallow, which involves swallowing a metallic liquid known as barium and using X-rays to highlight potential areas of concern
- CT scans of the stomach, with or without the use of dye
- biomarker testing, which checks for the presence of certain genes, proteins, and other substances in biopsied tissue to help diagnose cancer
Additional testing can help stage cancer after diagnosis. Staging tests may include:
- endoscopic ultrasound
- MRI with gadolinium
- laparoscopy, a surgical procedure to look at the organs in the abdomen
- PET-CT scan
Learn more about diagnosing stomach cancer.
What are the obvious signs of stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer often does not cause any symptoms in early stages. Even at later stages, symptoms may be nonspecific but
How often is cancer found during endoscopy?
An endoscopy is an accurate tool for stomach cancer diagnosis, particularly when doctors combine it with a biopsy. It can detect about 70% of cases with the first endoscopy and biopsy, and about 98% with 7 biopsies.
An endoscopy can help a healthcare professional find and diagnose stomach cancer.
Combined with a biopsy, it is a very effective method in diagnosing stomach cancer by allowing medical professionals to detect and assess lesions, ulcers, and other abnormalities in the stomach wall.
Doctors may recommend endoscopy if a person is at high risk of stomach cancer or if they have symptoms of the condition. The doctor can provide more information about what the test involves and what a person’s test results may mean.


